Sometimes, a functioning website unavailable by domain name. This happens due to incorrect settings, and in this article, we will explore why a site does not open by its domain name and what to do about it.
It sometimes happens that everything seems to be configured properly, but the domain is not working and the website is unavailable. In order for a website to be available by its domain name, it should be transformed into an IP address of the web server where the website is hosted. Global domain name system (DNS) is responsible for that. In order to successfully transform a domain into IP address the following conditions should be fulfilled:
- The domain should be registered and delegated;
- Servers of those domains that the management of the domain extension was delegated to should properly send the IP address of the web server;
- High-level DNS servers should contain information about the domain that is up-to-date;
If at least one of the conditions above is not fulfilled correctly, the website will be unavailable.
Let’s take a closer look at how it works and some basics of diagnostics at each stage.
How to register and delegate a domain
Domain registration is performed after the purchase. Basically, all you do is send your domain information to the high-level domain extension registry.
Delegation is handover of domain extension management to a certain domain server. In order to delegate a domain one should enter the addresses of DNS servers where resource records of this domain will reside. Most of the time DNS servers addresses are provided by the domain or hosting provider when you purchase a domain. As a rule, there are only two servers. All actions can be performed through administration panel. You should get the access to it after the purchase.
In order to check the status of a domain you can use any Whois service. For example, use this one: whois.com. If the domain is already registered, you will see all the information about it.
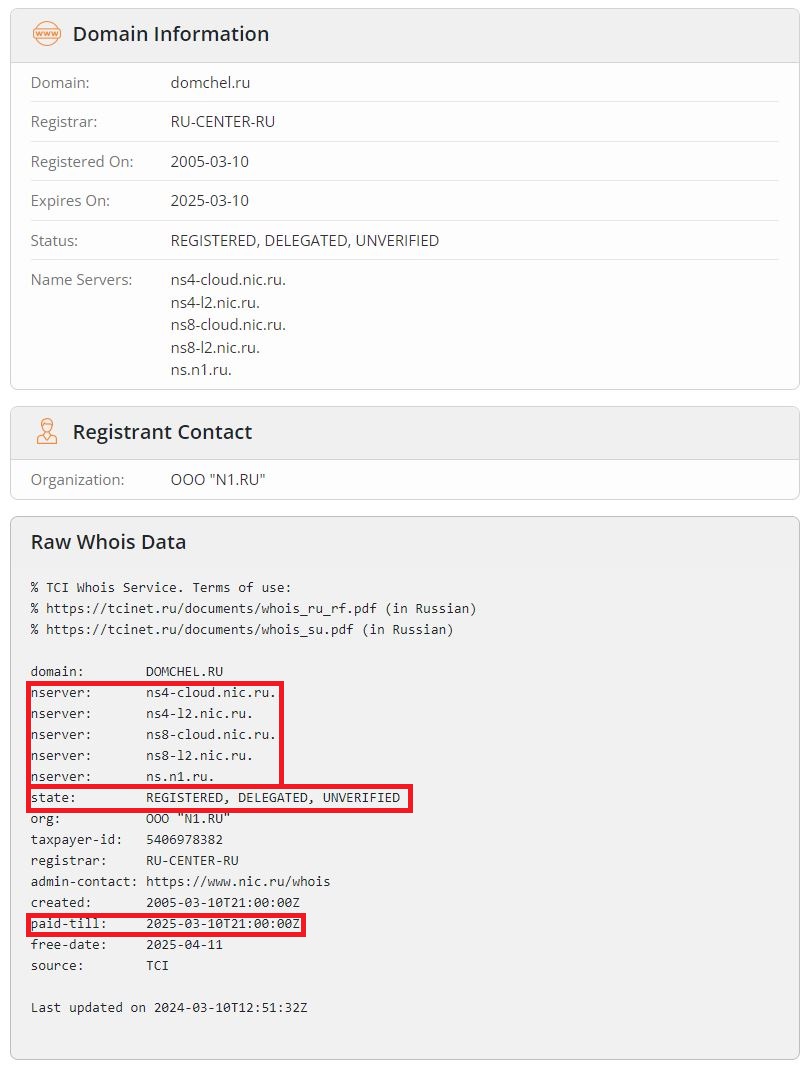
Take a look at the following fields:
- «paid-till» — the date until the domain is paid. Make sure that the date is still valid. If the domain is not paid until the date, it will become blocked. If they don’t receive the payment within a month, the domain becomes available for purchase.
- «state» — статус. You need to make sure that the domain has status «REGISTERED» or «DELEGATED». It means that domain is registered or delegated.
- «nserver» — DNS servers addresses that the domain extension management was delegated to. You need to make sure that the DNS servers are correct. As mentioned above, these addresses are usually provided after purchase by your domain or hosting provider.
If you get «Domain is available» message, it means that the domain is not registered and further checks make no sense, because you need to purchase the domain first. Despite everything is quite obvious, inexperienced users may make certain mistakes while trying to connect hosting with a non-existent domain.
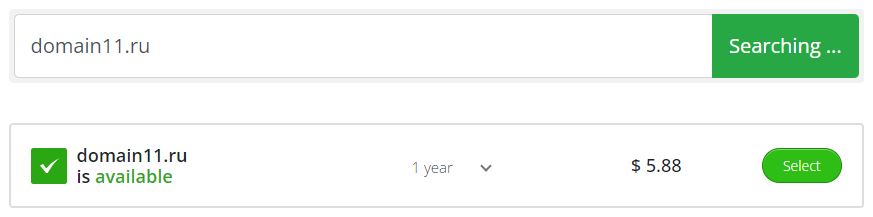
If at this stage everything is OK with the domain, you can proceed to the next step.
DNS servers check
Domain names servers that were delegated domain management to should return resource records of the domain extension by request. Resource records is a service information about the domain that’s stored on the DNS server. There are different types of resource records. We only need the most frequently used type «А» record that defines what IP address corresponds to the domain. If you’re purchasing domain and hosting from one provider, resource records can be created automatically.
If you have to deal with two different providers, you should create them manually from the administration panel that your provider should give you access to. Take a look at the resource records of the «domain111.ru» domain on the screenshots from DNSManager panel from ISPsystem company. By the way, we have a related article here "How to create and setup DNS records in DNS Manager"
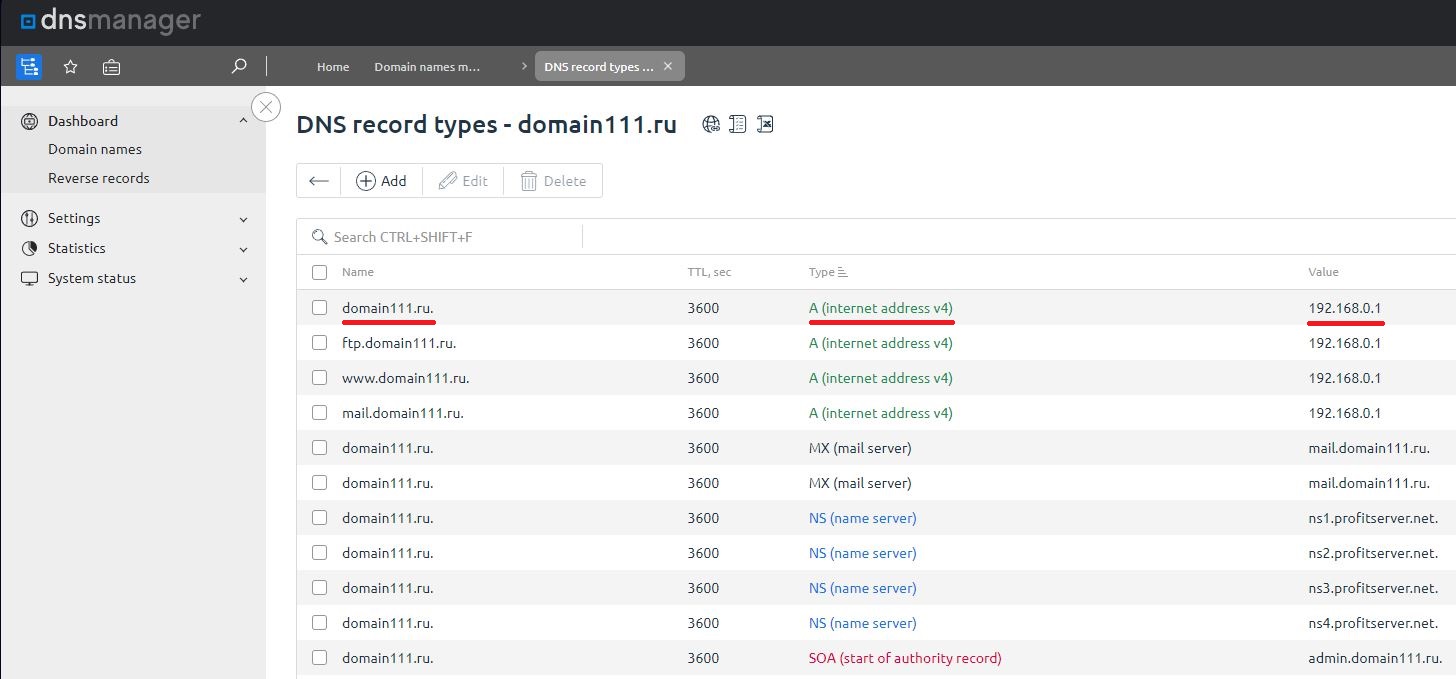
At this stage the point is to make sure that the DNS server that the domain extension management was delegated to gives out the type «А» record, i.e. IP address of the domain. To check that use this command line utility «nslookup».
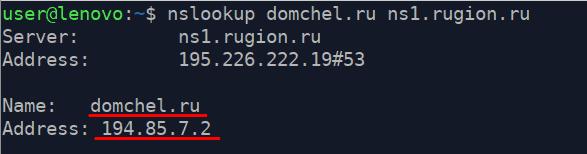
Let’s take a look at the diagnosis process and take «domchel.ru» domain as an example. «Whois» service shows that the domain extension was delegated to these DNS servers: «ns1.rugion.ru» and «ns2.rugion.ru», which means that each of them should contain type A record of this domain and give it out by request, so let’s check it.
Let’s open the command line and run «nslookup domchel.ru ns1.rugion.ru», where the first parameter is your domain name, and the second one is the DNS server that the request will be addressed to. The utility requests type А record by default, that’s why there’s no “type” parameter. If the DNS service returns domain name and IP address (as on the screenshot) everything’s well.
Let’s check once again with a non-existent domain name.
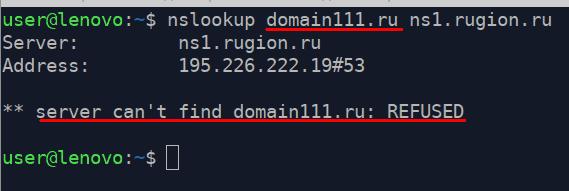
The server couldn’t find the requested domain in it’s database.
If the DNS server couldn’t find your domain in its database, first thing you should do is to check if there is type A record in the administration panel. If it’s there, contact support service of the provider. It’s more likely that the problem is on their side and is connected with the domain name server.
But if this test is successful, proceed to the next step.
High-level DNS servers update
Long story short, global domain names system works like this: high-level DNS servers contain information about lower-level DNS servers. Thus, it means (as on our example above «domchel.ru») that all servers of the «ru» extension should contain information about «domchel.ru» being serviced by ns1.rugion.ru and ns2.rugion.ru DNS servers.
Considering the fact that the state of low-level domains constantly changes (domains are registered, become available for purchase, delegated to other DNS servers, change IP addresses of their hostings) the high-level database of DNS servers should always be updated.
As a rule, after delegation of a domain and creation of the records this information is distributed around the network within a day. Only after that your domain becomes available from anywhere globally. At this stage, all that a user needs to do is wait. If it takes longer than one day, but your website is still unavailable, check it once again with nslookup. Run the same command but use any public DNS server, for example 8.8.8.8 — this is Google’s public DNS server.
Let’s run this command: «nslookup domchel.ru 8.8.8.8»
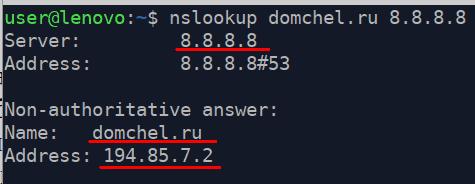
If the public server returned IP address of the domain as seen on the screenshot, it means that the information about your domain is already spread around the network.
If enough time passed but public DNS servers still can not find your domain, contact your provider’s support service. Apparently, there is a problem with data transfer to high-level name servers.
Besides the test with public DNS servers, you can check local domain name server that’s in your PC’s network settings. There’s a chance that the problem is with your network adapter configuration on your PC or with DNS servers of your Internet provider.
Let’s run this command «nslookup domchel.ru» If command does not contain correct domain name server the request will be addressed to the local DNS server.
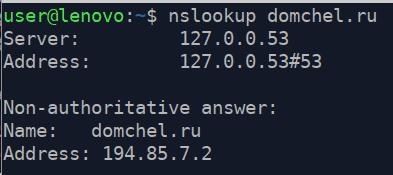
When public name servers «know» IP address of your website, but the local server keeps responding that the domain is not found, it means that the problem is in your network adapter configuration on your PC or your Internet provider’s DNS server.
If after you run the command you receive your domain’s IP address, it means that the domain name transformation is successful at all levels.
The actions described above will help you diagnose the problem and see if it’s connected with the domain name system or not.